Recently Google have released an evolutionary search strategy for scaling inference time compute in Large Language Model called Mind Evolution, uses a language model to generate, recombine and refine candidate responses. The proposed approach avoids the need to formalize the underlying inference problem whenever a solution evaluator is available.
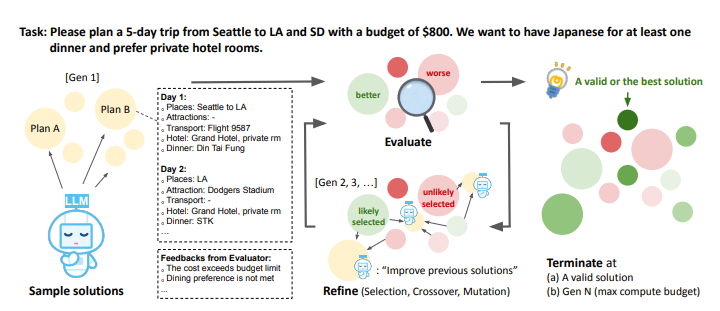
Mind Evolution is a genetic search strategy that evolves a diverse population of candidate solutions, leveraging an LLM to generate, recombine and refine solution candidates based on feedback from an evaluator. The overall process is analogous to combining divergent thinking (free-flowing parallel idea exploration) with convergent thinking (idea evaluation and selection), considered as hallmarks of intelligent problem solving behavior.
The core components of Mind Evolution involved: (1). the specific choices for the selection and migration operations; (2). the set of prompts that implement the initialization, recombination (crossover and mutation), and island reset operations with an LLM; (3). the fitness function that evaluates the quality of a given solution and optionally provides feedback on issues detected. The overall evolution process is repeated until a valid solution is found, or until 𝑁gens generations have been completed, after which the best scoring candidate is returned.
For instance let consider an example problem from the Trip Planning task in Natural Plan, with the predicted plans from Mind Evolution and the baselines. 1-Pass and Best-of-N both make mistakes on the number of days to stay, but satisfy the requirements of being in Madrid and Santorini on specific days. The Sequential-Revision+ plan omits the annual show in Madrid and plans a non-existent flight, but is correct in the number of days. In contrast, the Mind Evolution plan satisfies all specified requirements
Controlling for inference cost, It was found that Mind Evolution significantly outperforms other inference strategies such as Best-of-N and Sequential Revision in natural language planning tasks.